If you’re wondering how to upgrade processor in a laptop, you’ve likely reached a frustrating point where your trusty machine struggles with tasks it once handled with ease. Before you start shopping for a new one, the idea of a ‘heart transplant’ for your machine – a CPU upgrade – is tempting. Over my decade of hands-on hardware experience, I’ve seen this project be both incredibly rewarding and a complete waste of time and money. That’s why this guide is different.
Instead of just showing you the ‘how,’ I’m going to first help you answer the most important questions.
- Should you? Is a CPU upgrade the right financial and practical decision for you?
- Can you? Is your specific laptop even technically capable of being upgraded?
- How do you? What is the exact, safe process for performing the replacement?
1. The critical first step: Should you upgrade or replace?
This is, without a doubt, the most important section of this article. A successful upgrade can feel like getting a new laptop for a fraction of the price, but a failed or pointless one is far worse than just buying a new machine. Answering ‘Is it worth upgrading a laptop processor?’ depends entirely on your specific situation.
To help you make a sound decision, I’ve created this comparison table outlining the key factors to consider.
| Factor | Upgrade CPU | Buy New Laptop |
|---|---|---|
| Total Cost | Low to Moderate ($50 – $300+) | High ($500 – $2000+) |
| Potential Performance Gain | Varies wildly (10% – 50%). Limited by other old components. | Significant. All components are new and balanced. |
| Time/Effort Involved | High. Requires research, disassembly, and technical skill. | Low. Just data transfer and setup. |
| Risk Level | High. Risk of permanent damage to the laptop. | Very Low. Covered by manufacturer warranty. |
| Future-Proofing | Low. You’re still using an old motherboard, RAM, and chassis. | High. Modern ports, faster memory, and a new battery. |
1.1. Your interactive decision checklist
Before you even think about buying parts, let’s run through a quick self-assessment. This checklist is designed to give you a clear ‘go’ or ‘no-go’ signal for your potential laptop CPU upgrade project.
- Is your laptop more than 5 years old? (If yes, other components like the motherboard and RAM are significant bottlenecks, making a new laptop a better investment.)
- Is your current CPU already the top model offered for your laptop series? (If yes, there’s likely no compatible upgrade path.)
- Is your primary goal to improve gaming performance? (If yes, you’re almost always better off with a new laptop, as the GPU, which is not upgradeable, is more important.)
- Are you uncomfortable with the idea of completely disassembling your laptop? (If yes, this project is not for you. It is an invasive procedure.)
- Is your budget for the upgrade less than $50? (If yes, you likely won’t find a processor that provides a meaningful performance boost.)
If you answered ‘No’ to 3 or more of the questions above, a CPU upgrade is likely a viable and rewarding project for you. If not, I strongly recommend you consider upgrading your RAM/SSD first or replacing the laptop entirely.
1.2. Setting realistic expectations: What performance gains will you actually see?
A new CPU won’t magically make your old laptop outperform a new one. The impact of the upgrade depends heavily on the tasks you perform. A faster processor will primarily help with CPU-intensive tasks like video rendering, code compiling, or running complex calculations.
Here is a table to help you set realistic expectations for what kind of boost you might see when looking for the best laptop processors for an upgrade.
| Task | From Core i3 to i5 | From Core i5 to i7 (Same Generation) |
|---|---|---|
| Web Browsing | Minor boost, smoother multitasking | Barely noticeable |
| Office Apps | Slightly faster load times | Very minor improvement |
| 1080p Gaming | Minor boost to minimum frame rates | Minor to moderate improvement, depending on the game |
| Video Rendering | Significant improvement (~30%) | Significant improvement (~25-40%) |
To quantify your results, I highly recommend running a free benchmark like Cinebench or Geekbench before you start. This gives you a baseline score to compare against after the upgrade, so you can see exactly what your hard work achieved.
2. The technical reality check: How to know if your laptop CPU is upgradeable
Now we get to the technical heart of the matter. Before we go any further, I need to state the hard truth: the single most important factor determining if you can upgrade your laptop’s CPU is whether it’s soldered to the motherboard or sits in a removable socket. Most modern, thin-and-light laptops have soldered CPUs to save space, making an upgrade impossible. Older, thicker, or gaming-oriented laptops are more likely to have a socketed, replaceable CPU.
The core question you must answer for your device is: Is my CPU soldered or socketed? Finding this out is your next critical step in determining your laptop upgrade compatibility. Answering ‘Can you change laptop processor?’ for your specific model requires research, which I’ll detail in the next section. But the socket isn’t the only hurdle.
2.1. Beyond the socket: Chipset, power, and BIOS limitations
Even if your CPU is in a socket, you can’t just drop in any processor that fits. Several other factors determine your motherboard compatibility and can stop an upgrade in its tracks.
- Chipset Compatibility: The motherboard’s chipset is like a traffic controller, designed to work with a specific family of CPUs. You can only upgrade to a CPU that is supported by your existing chipset. For example, you can’t put a 9th-generation Intel CPU on a motherboard designed for 4th-generation CPUs.
- Thermal Design Power (TDP): This is a measure of the maximum heat a CPU generates. Think of TDP as a light fixture’s maximum wattage rating. You can’t put a 100-watt bulb in a socket rated for 60 watts without causing problems – the same goes for a CPU that generates more heat than your laptop’s cooling system can handle. You must choose an upgrade with a similar or identical TDP to your current CPU to avoid overheating.
- BIOS Whitelisting: Some manufacturers, particularly in the past, programmed the laptop’s BIOS to only accept a specific list of pre-approved CPUs. Even if a processor is compatible in every other way, the laptop may refuse to boot with it if it’s not on this ‘whitelist’.

3. Finding the perfect match: Which CPUs are compatible with your laptop?
This section is where your research begins. To find a compatible CPU, you first need to gather two key pieces of information: your exact laptop model number (usually found on a sticker on the bottom of the case) and your current CPU model (which you can find in Windows by right-clicking the Start button and selecting ‘System’). With this information, you can begin the hunt.
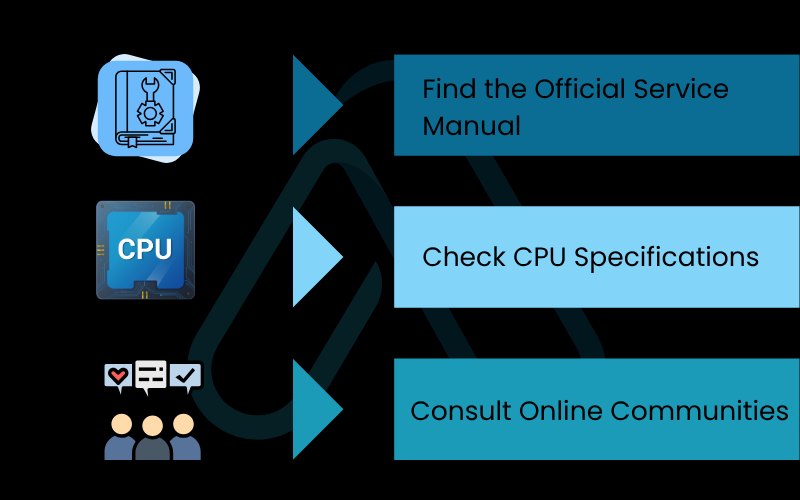
Here is my proven process for determining your laptop upgrade compatibility.
- Find the Official Service Manual: This is the most reliable source of information. Search online for `”[Your Laptop Model]” service manual` or `maintenance manual`. This document, created by the manufacturer, will list all Field Replaceable Units (FRUs), including every CPU model that was ever offered for that chassis. This is your definitive compatibility list.
- Check CPU Specifications: Once you have a list of compatible CPUs from the manual, look them up on the manufacturer’s website (e.g., Intel Ark or AMD’s spec pages). Confirm that the socket type matches and compare the TDP. Stick to CPUs with the same TDP as your current one.
- Consult Online Communities: Search forums like Reddit (r/laptops) or NotebookReview for posts from other users who have the same laptop model. They may have already successfully performed an upgrade and can confirm which processors work.
3.1. Manufacturer-specific compatibility guides (Dell, HP, Lenovo)
Finding the right documentation can vary by brand. Here’s my quick guide for the major players.
Dell Laptops
For Dell, your best bet is to go to their support website and enter your laptop’s Service Tag. Look for the ‘Documentation’ or ‘Manuals’ section and find the ‘Service Manual’. This document is the gold standard for Dell hardware information.
HP Laptops
HP provides excellent ‘Maintenance and Service Guides’ for most of its models. Searching for `”[Your HP Model]” maintenance and service guide` will usually lead you directly to a PDF that contains a full list of compatible parts, including processor options. This is essentially an HP laptop CPU compatibility chart.
Lenovo Laptops
Lenovo’s ‘Hardware Maintenance Manual’ (HMM) is what you’re looking for. Search for your model on Lenovo’s support site to find the HMM, which will contain the crucial list of compatible CPUs and their part numbers.
3.2. Where to safely buy a replacement CPU
Once you’ve identified a compatible CPU, you need to source it. A safe laptop CPU replacement starts with a reputable seller.
Here are the most common places to look, along with my advice.
- eBay: This is the most popular source for used laptop CPUs. You can often find great deals, but they carry risk. Look for experienced sellers with high ratings and a good return policy.
- AliExpress: Another option for used or refurbished processors, often at very low prices. Shipping times can be long, and returns can be difficult, so this is for the more patient and risk-tolerant upgrader.
- Dedicated Parts Suppliers: Websites that specialize in laptop parts may carry CPUs, but they are often more expensive. The benefit is usually better testing and more reliable customer service.

Buyer Beware: Always check seller ratings and return policies. Buying used CPUs carries a risk of receiving a dead-on-arrival (DOA) or a damaged part. Pay with a service that offers buyer protection.
4. The step-by-step guide: How to upgrade processor in a laptop
You’ve done the research and sourced your part. Now it’s time for the procedure itself. I must preface this with a critical disclaimer: performing this upgrade will void your warranty and carries a significant risk of permanently damaging your laptop if done incorrectly. Proceed with caution and at your own risk. This guide provides a general overview; your specific laptop may have different steps, so always refer to its service manual.
4.1. Essential tools and preparation
Before you remove a single screw, gather your tools and prepare your workspace.
Here’s what you’ll need for a safe laptop CPU replacement:
- Phillips #0 or #00 screwdriver
- Plastic spudger or prying tool
- High-quality thermal paste
- 90%+ isopropyl alcohol and lint-free cloths (for cleaning)
- An anti-static wrist strap
- A small container to organize screws
| CRITICAL Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can instantly destroy computer components. Work on a non-conductive surface and wear an anti-static wrist strap connected to a metal part of the laptop’s chassis throughout the entire process. Also, make sure you have a complete backup of your important data before you begin. |
4.2. The replacement process: Disassembly and installation
With your tools ready and precautions taken, it’s time to begin. Always keep your service manual handy.
- Disconnect Power and Battery: Unplug the AC adapter and remove the battery. If the battery is internal, you must disconnect it from the motherboard as soon as you open the case.
- Open the Chassis: Remove the screws from the bottom of the laptop case and carefully use a plastic spudger to release the clips holding the bottom panel in place.
- Access the CPU: The CPU is located under the heatsink and fan assembly. You will need to carefully disconnect the fan cable and unscrew the heatsink. The screws are often numbered, so unscrew them in reverse order (e.g., 4, 3, 2, 1) to release pressure evenly. Gently lift the heatsink off the CPU.
- Clean the Heatsink: Use isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free cloth to thoroughly clean the old thermal paste off the bottom of the heatsink.
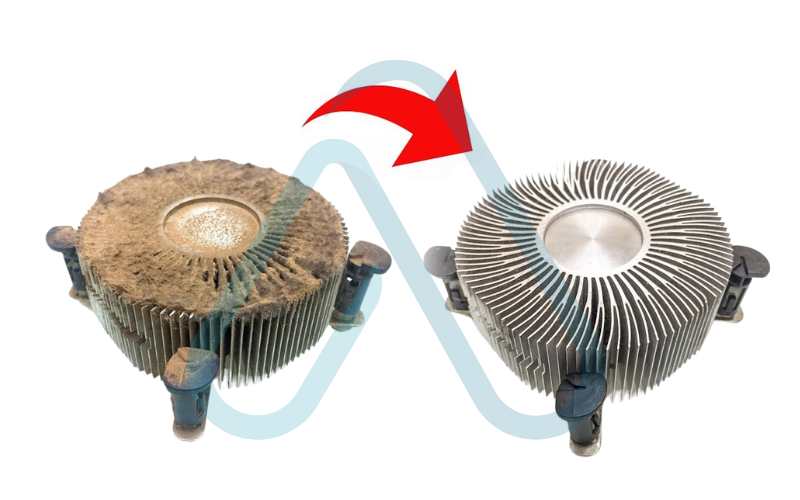

5. Unlock and Remove the Old CPU: The CPU is held in its socket by a small locking mechanism. This is typically a single flat-head screw that you turn 180 degrees to unlock. Once unlocked, you can carefully lift the old CPU straight out of the socket. Do not touch the pins on the bottom.
6. Install the New CPU: Carefully align the new CPU with the socket – there is a small triangle on one corner of the CPU that must match a triangle on the socket. Gently place it in the socket. It should drop in with zero force. Once it’s seated, turn the locking screw 180 degrees back to its original locked position.
7. Apply New Thermal Paste: Apply a pea-sized dot of new thermal paste to the center of the new CPU. Do not spread it; the pressure from the heatsink will do this evenly.
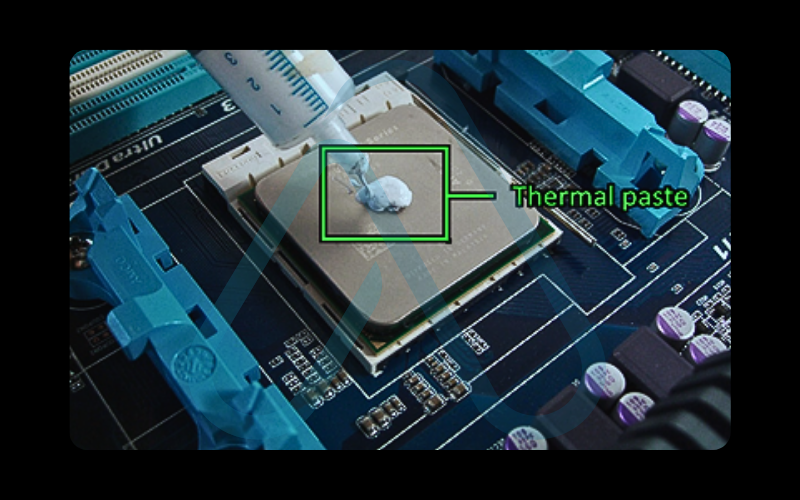
8. Reassemble: Reinstall the heatsink, tightening the screws in the numbered order (e.g., 1, 2, 3, 4). Reconnect the fan, reconnect the battery if it was internal, and secure the bottom case.
4.3. Understanding and mitigating the risks
Even when you’re careful, things can go wrong. Being aware of the risks helps you prevent them. Here is a summary of the primary risks and how to mitigate them.
- Risk: Electrostatic Discharge (ESD).
Mitigation: Always wear an anti-static wrist strap connected to the laptop’s frame. - Risk: Bent CPU pins.
Mitigation: Handle the CPU only by its edges and never touch the pins. Place it into the socket with zero force. - Risk: Cracking the CPU die.
Mitigation: Tighten and loosen the heatsink screws evenly in a cross pattern as indicated by their numbering. - Risk: Overheating.
Mitigation: Use a high-quality thermal paste and ensure the heatsink is seated correctly and makes full contact. - Risk: Voiding your warranty.
Mitigation: Understand that opening your laptop to this extent will void any active warranty.
5. After the upgrade: The crucial software checklist
Your job isn’t done once the case is closed. To ensure stability and get the full performance of your new hardware, you need to properly introduce your laptop’s software to its new brain. This is a non-negotiable step for a successful laptop BIOS update after a hardware upgrade.
Follow this checklist in order.
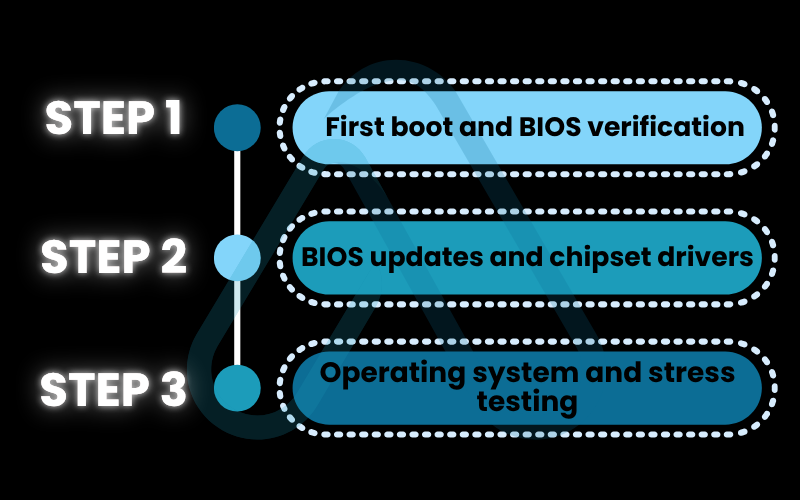
5.1. Step 1: First boot and BIOS verification
The first boot is a moment of truth. Here is what you need to do immediately.
- Power on the laptop. It may take longer than usual to boot for the first time.
- Immediately press the key to enter the BIOS/UEFI setup (often F2, F10, or DEL during startup).
- Navigate to the ‘Main’ or ‘System Information’ screen and verify that the new CPU model and speed are listed correctly. If they are, you can proceed. If not, power down and double-check your installation.
5.2. Step 2: BIOS updates and chipset drivers
Proper driver and firmware support is essential for your new CPU.
| Warning A failed BIOS update can render your laptop unusable. Ensure the laptop is plugged into AC power and do not interrupt the process. |
Go to your laptop manufacturer’s support website, find your model, and download the latest BIOS version. Follow their instructions precisely. After the BIOS is updated, download and install the latest chipset drivers for your motherboard to ensure the operating system can communicate effectively with the new processor.
5.3. Step 3: Operating system and stress testing
Finally, let’s make sure everything is stable under pressure. These are the final checks I always perform.
- Once you boot into Windows, open Device Manager and ensure there are no errors listed under the ‘Processors’ category.
- Run a stress test utility like Prime95 and a temperature monitoring tool like HWMonitor simultaneously for at least 30 minutes.
- Watch the temperatures closely. If they climb above 95°C, stop the test immediately. This indicates a problem with your thermal paste application or heatsink installation.
6. Simpler alternatives: Other ways to boost laptop performance
After reading through the process, you may have decided that a CPU upgrade is too risky or simply not possible because your processor is soldered. That’s a perfectly valid conclusion. For many users who come to me for advice, I often recommend two far simpler, cheaper, and safer upgrades that can have a massive impact on day-to-day performance.
Upgrading Your RAM
If your laptop has less than 16GB of RAM, upgrading it is the single best thing you can do to improve multitasking performance. It allows you to have more browser tabs, applications, and background processes running without your system slowing to a crawl. This is a simple, 15-minute upgrade on most laptops.
Switching to a Solid State Drive (SSD)
If your laptop still uses a mechanical hard disk drive (HDD), upgrading to an SSD is a night-and-day difference. Your laptop will boot in seconds, applications will launch instantly, and the entire system will feel incredibly responsive. It’s the most noticeable performance upgrade you can make.
7. FAQs about how to upgrade processor in a laptop
Here are quick answers to some of the most common questions I get about this topic.
Can you upgrade the processor on any laptop?
No. Most modern laptops have soldered CPUs, so only some older or high-end models with socketed processors can be upgraded.
How do I know if my laptop CPU is upgradeable?
Check the official service manual; it will show if the CPU is soldered or socketed and list compatible models.
Is it worth upgrading a laptop’s processor?
Only if it’s a newer laptop with a socketed CPU and affordable upgrade options. Otherwise, buying a new laptop is better.
What risks are involved in changing a laptop CPU?
Risks include ESD damage, motherboard or CPU breakage, overheating, and voiding your warranty.
Which CPUs are compatible with my laptop?
Only those listed in the laptop’s service manual that match the socket, chipset, cooling, and BIOS support.
Glossary of key terms
| Abbreviation | Full Term | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| BIOS | Basic Input/Output System | Firmware used to perform hardware initialization during the booting process on older PCs. |
| Chipset | N/A | A set of electronic components on a motherboard that manages the data flow between the processor, memory, and peripherals. |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit | The primary component of a computer that performs most of the processing. The ‘brain’ of the computer. |
| DOA | Dead on Arrival | The sudden flow of electricity between two objects which can permanently damage sensitive electronics like CPUs. |
| ESD | Electrostatic Discharge | The sudden flow of electricity between two objects can permanently damage sensitive electronics like CPUs. |
| FRU | Field Replaceable Unit | A part or component of a computer that can be easily replaced by a user or technician. |
| HMM | Hardware Maintenance Manual | Lenovo’s term for a service manual that details hardware components and replacement procedures. |
| RAM | Random-Access Memory | A form of computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data. |
| SSD | Solid-State Drive | A storage device that uses flash-based memory, which is significantly faster than a traditional mechanical hard drive. |
| TDP | Thermal Design Power | The maximum amount of heat generated by a computer chip or component that the cooling system is designed to dissipate. |
| UEFI | Unified Extensible Firmware Interface | A modern specification for computer firmware that replaced the traditional BIOS. |
8. Final thoughts
Upgrading a laptop’s CPU can be a deeply rewarding project that breathes new life into an old machine. In my experience, it’s a technical challenge that demands careful research, patience, and preparation. It is not a simple fix for a slow computer, but rather a project for a knowledgeable enthusiast. Before you ever pick up a screwdriver, be honest with yourself about the risks, costs, and potential rewards.
Here are my most critical takeaways from this guide on how to upgrade processor in a laptop:
- Decision first, action second: Always determine IF you should and CAN upgrade before you even think about HOW to do it.
- The service manual is your bible: Your laptop’s official maintenance manual contains the definitive list of compatible parts. Trust it above all else.
- Safety is paramount: Electrostatic discharge is a silent killer of components. An anti-static wrist strap is not optional.
- Consider the alternatives: For many users, a RAM or SSD upgrade will provide a more noticeable performance boost for less money, effort, and risk.
I hope this guide has empowered you to make an informed decision. For more in-depth guides, explore our Productivity & Automation categories on Afdevinfo.