When I’m asked what do you learn in cyber security, I often see a mix of excitement and overwhelm in people’s eyes. The world of cybersecurity can feel like a vast, complex maze. You know it’s important, but where do you even begin? After more than a decade in this field, I’ve seen countless beginners get lost in endless lists of tools and topics. That’s why I created this guide. It’s designed to be different.
This guide isn’t just a list of topics; it’s a personalized roadmap to help you find your unique path in cybersecurity.
My goal is to help you move from feeling overwhelmed to feeling empowered. We’ll start by figuring out if this field is a good fit for your personality, then map out a clear learning pathway based on your background and ambitions.
1. First, is cybersecurity the right field for you? a self-assessment
Before diving into the technical details, I believe it’s crucial to look inward. Success in cybersecurity isn’t just about technical chops; it’s about a certain mindset. I’ve designed this short, no-pressure quiz to help you see how your natural tendencies align with different roles in this field.
When a complex problem arises, what is your first instinct?
- To break it down into the smallest possible pieces to find the root cause.
- To think about building a system or a process to prevent it from happening again.
- To consider the bigger picture: How does this affect our goals and what are the risks?
You come across a new piece of technology. What do you do?
- Try to figure out how it works, what its weaknesses are, and how it could be exploited.
- Think about how I could use it to improve a current system or make something more efficient.
- Assess its potential impact, both positive and negative, on the organization.
How do you approach rules and procedures?
- I need to understand the ‘why’ behind a rule to follow it effectively. I enjoy looking for exceptions.
- I value clear rules and well-designed processes that ensure consistency and security.
- I’m interested in creating and enforcing the rules that protect the organization and its data.
A small detail seems out of place in a large dataset. How do you react?
- I become intensely curious and will dig until I understand why it’s there.
- I note it and consider how our systems could be improved to catch such anomalies automatically.
- I immediately start thinking about what this anomaly could mean from a risk perspective.
5. What statement best describes your primary motivation?
- The thrill of the hunt and solving a complex puzzle.
- The satisfaction of building secure, resilient, and reliable systems.
- The responsibility of protecting assets and ensuring the organization operates safely.
1.1. What kind of cybersecurity mind do you have?
Based on your answers, you’ll likely lean towards one of three core mindsets. It’s important to remember that these are not rigid boxes; they are guides to help you find a starting point. All these mindsets are incredibly valuable in cybersecurity.
- Mostly A’s – The Investigator: You have the analytical and curious mind of a security analyst or penetration tester. You enjoy deconstruction, finding hidden clues, and understanding the ‘how’ and ‘why’ behind security events. You are drawn to the detective work of cybersecurity.
- Mostly B’s – The Builder: You possess the systematic and proactive mindset of a security engineer or architect. You enjoy creating, fortifying, and maintaining secure systems. Your satisfaction comes from building digital fortresses that withstand attacks.
- Mostly C’s – The Strategist: You have the holistic and risk-focused mindset for a role in Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC). You excel at understanding the big picture, creating policies, and aligning security efforts with business objectives.
Now that you have an idea of your natural inclination, let’s look at the learning pathways that align with these mindsets.
2. Finding your cybersecurity skill pathway
One of the biggest mistakes I see beginners make is trying to learn everything at once. The key to success is realizing that cybersecurity learning isn’t one-size-fits-all. The best path for a software developer is different from the path for a project manager or a complete newcomer. Understanding the major cybersecurity career paths is the first step toward building your knowledge of cybersecurity fundamentals.
Based on the self-assessment and your personal background, I’ve broken down the learning journey into three main pathways. Find the one that resonates most with you.
2.1. For the future technical specialist (the engineer track)
This pathway is for you if you love taking things apart to see how they work, enjoy scripting, and want to be on the front lines building and breaking digital defenses. This track aligns with the ‘Builder’ and ‘Investigator’ mindsets and leads to hands-on technical roles like Security Engineer, Cloud Security Specialist, or Penetration Tester.
Here are the key skills I recommend focusing on for this track:
- Advanced Networking: Deep understanding of TCP/IP, routing protocols, and network architecture.
- Operating System Internals: In-depth knowledge of Linux and Windows systems, including command-line proficiency, file systems, and process management.
- Scripting & Automation: Proficiency in a language like Python or PowerShell to automate security tasks and analyze data.
- Cloud Security Fundamentals: Understanding the security models of major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or GCP.
- Cryptography Concepts: Grasping the principles of encryption, hashing, and digital signatures.
2.2. For the aspiring security analyst (the analyst track)
This is the most common entry point for those with some existing IT knowledge or those who align with the ‘Investigator’ mindset. If you’re transitioning from a helpdesk or network admin role, this is your sweet spot. This path prepares you for roles like Security Operations Center (SOC) Analyst, Threat Intelligence Analyst, or Incident Responder.
The focus here is less on building and more on monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats.
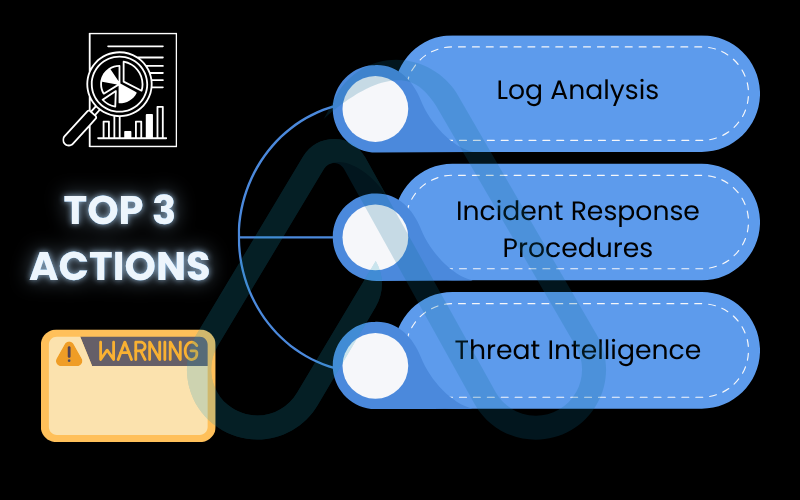
For aspiring analysts, I always recommend prioritizing these top 3 skills:
- Log Analysis: The ability to read, interpret, and find anomalies in logs from various sources (firewalls, servers, applications) is the single most important skill for an analyst.
- Incident Response Procedures: Understanding the formal process of how to handle a security incident, from initial detection to final resolution.
- Threat Intelligence: Learning how to consume and apply information about current threats, attacker techniques, and vulnerabilities to improve your organization’s defenses.
2.3. For the business professional (the grc track)
Cybersecurity isn’t just for techies. This pathway is perfect for career-switchers from fields like law, project management, finance, or auditing who align with the ‘Strategist’ mindset. Your existing skills in communication, policy, and risk management are incredibly valuable here. This track leads to roles like Security Auditor, Compliance Manager, or Risk Analyst.
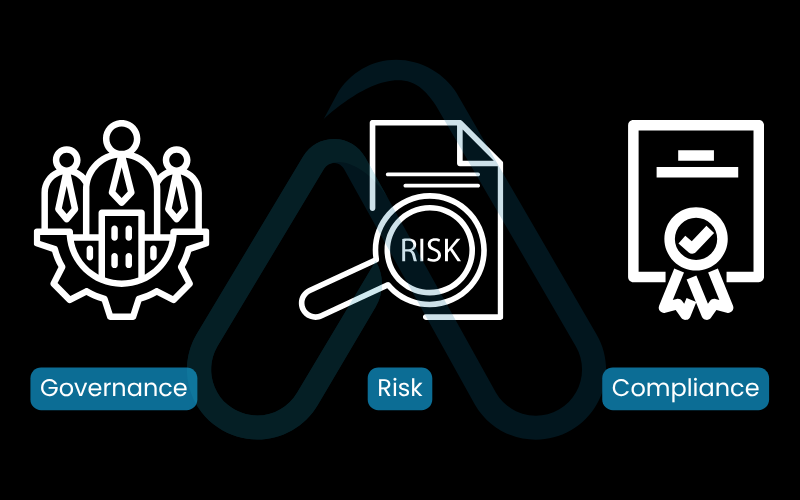
This path demystifies the business side of security. Here’s what GRC involves:
- Governance: This is about creating the rules. It involves developing security policies, standards, and procedures that guide how an organization protects its information.
- Risk: This is about identifying the threats. It involves assessing potential security weaknesses, calculating their potential impact, and deciding how to manage them (accept, mitigate, transfer, or avoid).
- Compliance: This is about following the rules. It involves ensuring the organization adheres to legal and regulatory requirements, like GDPR for data privacy or HIPAA for healthcare information.
3. The core topics in cybersecurity you will learn: building your foundational knowledge
Regardless of the pathway you choose, there are foundational pillars of knowledge that every cybersecurity professional must understand. My approach has always been to build from the ground up. Think of it like building a house; you need a solid foundation of IT fundamentals before you can build the secure walls and roof.
3.1. Network and infrastructure security
I always tell beginners to start here. The network is the digital city where everything happens. Data is the traffic, routers are the intersections, and firewalls are the gatekeepers. Understanding the network security basics is non-negotiable because it’s the foundational layer where most cyber activity occurs.
| Why This Matters Now: Recent supply chain attacks often start by compromising a single network device. Understanding network security is the first line of defense against widespread breaches. |
Here’s a breakdown of what you’ll learn:
| Key Concepts | Why It Matters | Your First Step |
| TCP/IP Suite, DNS, Ports & Protocols | This is the fundamental language of the internet. You can’t secure what you don’t understand. | Learn the OSI model and how data flows from your browser to a web server. |
| Firewalls, VPNs, IDS/IPS | These are the primary tools used to control traffic and detect malicious activity on the network. | Set up a simple firewall on your own computer and understand its rules. |
| Network Segmentation & Access Control | This prevents an attacker who breaches one part of the network from accessing everything. | Read about the principle of least privilege and how it applies to networks. |
3.2. Application and data security
If the network is the city, applications are the buildings where valuable data is stored and processed. This domain focuses on building secure software and protecting the data itself, whether it’s at rest, in transit, or in use. The goal is to protect the crown jewels—the information that applications handle.
Here are some of the most common vulnerabilities you will learn to identify and prevent:
| Vulnerability | Simple Explanation |
| SQL Injection (SQLi) | Tricking an application into running unintended database commands to steal data. |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Injecting malicious scripts into a website that then run in other users’ browsers. |
| Broken Access Control | A flaw that allows a user to access data or perform actions they aren’t authorized for. |
Here’s a breakdown of what you’ll learn:
| Key Concepts | Why It Matters | Your First Step |
| Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SSDLC) | Building security into the development process from the start is cheaper and more effective than fixing it later. | Learn about the basic principles of the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities. |
| Encryption & Hashing | These are the core technologies used to make data unreadable to unauthorized parties. | Understand the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption. |
| Identity & Access Management (IAM) | Ensuring that only the right people have access to the right data at the right time. | Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on your personal accounts to see it in action. |
3.3. Threat intelligence and attack methodologies
To build better defenses, you have to think like an attacker. This part of cybersecurity is about understanding your adversary: who they are, what motivates them, and the tools and techniques they use. This is where you learn about the different types of cyber attacks and the frameworks used to analyze them.
Here’s a breakdown of what you’ll learn:
| Key Concepts | Why It Matters | Your First Step |
| Cyber Kill Chain & MITRE ATT&CK | These frameworks provide a structured way to understand and categorize the stages of a cyber attack. | Read through the 7 stages of the Cyber Kill Chain to understand an attack’s lifecycle. |
| Malware Types (Viruses, Ransomware, Trojans) | Understanding the different families of malicious software helps in detection and remediation. | Learn the key differences between a virus, a worm, and a trojan horse. |
| Social Engineering (Phishing, Vishing) | This is the art of manipulating people into giving up confidential information. It’s often the first step in a major breach. | Analyze a phishing email you’ve received and identify the red flags. |
3.4. Governance, risk, and compliance (grc)
This is the strategic brain of cybersecurity. It connects the technical work of security teams to the business objectives of the organization. GRC ensures that security efforts are consistent, managed, and aligned with legal and business requirements. For example, a hospital’s entire cybersecurity strategy is guided by its need to comply with HIPAA regulations to protect patient data.
Here are the three components of GRC:
- Governance: The framework of policies, roles, and responsibilities for security.
- Risk: The process of identifying, analyzing, and treating security risks.
- Compliance: The act of conforming to internal policies and external laws/regulations.
Here’s a breakdown of what you’ll learn about risk management in cybersecurity:
| Key Concepts | Why It Matters | Your First Step |
| Security Policies & Standards | These documents provide the official rules for security within an organization. | Look up a sample ‘Acceptable Use Policy’ online to see how they are structured. |
| Risk Assessment & Management | This process helps organizations prioritize their security spending and efforts on the most critical threats. | Think about a simple risk in your own life (e.g., losing your phone) and how you mitigate it. |
| Security Frameworks (NIST, ISO 27001) | These provide a comprehensive checklist and best-practice guide for building a security program. | Read a high-level overview of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF). |
4. From theory to practice: what hands-on skills do you learn in cyber security?
Knowing the theory is one thing, but getting hired requires proving what you can do. This section shifts our focus from ‘what you know’ to ‘what you can do.’ These are the practical, actionable skills that I see on job descriptions every single day.
Before we dive in, here is a summary of the top practical skills you’ll need to develop:
- Analyzing security logs for suspicious activity.
- Responding to a security incident according to a plan.
- Using vulnerability scanners to find weaknesses.
- Configuring security tools like firewalls and antivirus.
- Writing clear reports for both technical and non-technical audiences.
4.1. Incident response and handling
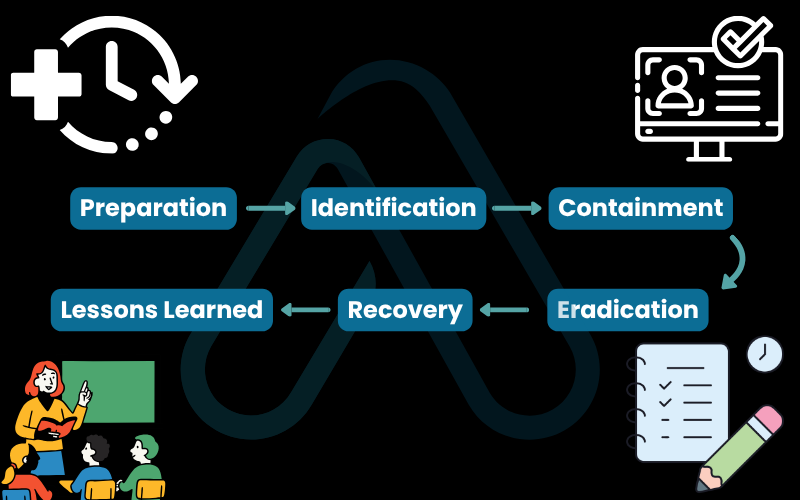
Imagine your company’s website suddenly goes down due to a cyber attack. What’s the first thing you do? Panic is not an option. Incident response (IR) is the formal playbook that guides you through the chaos. It’s a methodical process for managing the aftermath of a security breach to limit damage and reduce recovery time.
Here is the standard six-phase process you will learn to follow:
- Preparation: Getting your tools, processes, and people ready before an incident happens.
- Identification: Detecting a security event and determining if it is a genuine incident.
- Containment: Isolating the affected systems to prevent the attack from spreading further.
- Eradication: Removing the attacker’s presence and malware from the compromised systems.
- Recovery: Restoring the affected systems to normal operation safely.
- Lessons Learned: Analyzing the incident to understand what went wrong and how to prevent it from happening again.
4.2. Using security tools and technologies
A cybersecurity professional’s toolkit is vast, but you don’t need to master every tool at once. The key is to understand the *function* of each tool category. As a beginner, I’d recommend getting familiar with what these common tools do.
Here is a table of the most common tool categories:
| Tool Category | What It Does | Why It’s Essential |
| SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) | Collects, aggregates, and analyzes security logs from across the entire network. | It’s the central ‘pane of glass’ for spotting suspicious activity and investigating incidents. |
| Vulnerability Scanner | Proactively scans systems and applications for known security weaknesses. | Finds security holes before attackers do. |
| Firewall | Acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and an untrusted external network (like the internet). | The fundamental tool for controlling network traffic and blocking unauthorized access. |
| Antivirus / EDR (Endpoint Detection & Response) | Protects individual devices (endpoints) from malware and detects malicious behavior. | Secures the most common entry point for attacks: user computers. |
4.3. Implementing security best practices
Finally, a huge part of the job involves translating high-level principles into concrete, daily actions. These are the foundational tasks that prevent the majority of common attacks. Mastering these security best practices is a critical hands-on skill.
Here is a checklist of fundamental tasks every organization must perform:
| What | Why | |
| User Access Management | Ensuring users have only the minimum level of access (privilege) necessary to do their jobs. | This limits the damage an attacker can do if they compromise a user’s account. |
| Patch Management | The process of regularly applying updates (patches) to software and systems to fix known vulnerabilities. | Unpatched software is one of the most common ways attackers gain initial access. |
| Security Awareness Training | Educating employees about security threats like phishing and how to recognize them. | Humans are often the weakest link; training them turns them into a strong first line of defense. |
5. FAQs about what do you learn in cyber security
As you start this journey, it’s natural to have questions. Here are my answers to some of the most common ones I hear from aspiring cybersecurity professionals.
What should I learn first in cybersecurity?
Start with networking basics (TCP/IP) and core OS knowledge (Linux + Windows). These foundations come before everything else.
Is cybersecurity hard to learn for beginners?
It can feel challenging because the field is broad, but you don’t need to be a genius. Curiosity, persistence, and attention to detail matter more than prior knowledge.
What skills are required for a cybersecurity job?
Technical: network security, incident response, and using security tools (SIEMs).
Soft skills: problem-solving, clear communication, and attention to detail.
How do I start a career in cybersecurity?
Pick a pathway (Analyst / Engineer / GRC), build hands-on skills in a home lab/CTFs, and get a starter cert like Security+.
Glossary of key terms
| Abbreviation | Full Term | Meaning |
| TCP/IP | Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol | The foundational suite of communication protocols used to connect network devices on the internet. |
| DNS | Domain Name System | The system that translates human-readable domain names (like afdevinfo.com) into machine-readable IP addresses. |
| VPN | Virtual Private Network | A secure, encrypted connection over a public network, used to protect browsing privacy and data. |
| SQLi | SQL Injection | A type of cyber attack that targets databases by inserting malicious SQL code into application inputs. |
| XSS | Cross-Site Scripting | An attack where malicious scripts are injected into trusted websites, which then run on a victim’s browser. |
| SIEM | Security Information and Event Management | A software solution that aggregates and analyzes security data from various sources to detect threats. |
| EDR | Endpoint Detection and Response | A cybersecurity technology that continuously monitors and responds to threats on devices like laptops and servers. |
| GRC | Governance, Risk, and Compliance | An organizational strategy for managing security policies, identifying and mitigating risks, and adhering to regulations. |
| HIPAA | Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act | A US federal law that requires the protection of sensitive patient health information. |
| GDPR | General Data Protection Regulation | A regulation in EU law on data protection and privacy for all individuals within the European Union. |
| OWASP | Open Web Application Security Project | A non-profit foundation that works to improve the security of software, known for its Top 10 list of web vulnerabilities. |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology | A US agency that develops cybersecurity standards and guidelines, including the widely used Cybersecurity Framework (CSF). |
6. Final thoughts
Learning cybersecurity is a marathon, not a sprint. My goal with this guide was to give you more than just a list of topics; I wanted to provide you with a compass and a map. By understanding your own mindset and choosing a deliberate pathway, you can navigate this complex field with confidence and purpose.
Your cybersecurity journey starts not with memorizing a thousand acronyms, but with taking a single, well-chosen first step. Use your pathway to guide you.
I hope this roadmap has given you the clarity you need to get started. The field is challenging, rewarding, and more important than ever. Here are the most critical takeaways I want you to remember:
- Start with Self-Assessment: Aligning your learning with your natural interests (as an Investigator, Builder, or Strategist) is the key to long-term success.
- Choose a Pathway, Don’t Boil the Ocean: Focus on one track—Engineer, Analyst, or GRC—to build deep skills rather than shallow, broad knowledge.
- Master the Fundamentals: A deep understanding of networking and operating systems is the non-negotiable foundation for any cybersecurity role.
- Practice is Paramount: Theoretical knowledge is useless without hands-on skills. Build a lab, use the tools, and learn by doing.
At Afdevinfo, my mission is to make digital security accessible and understandable. Your journey is just beginning, and we are here to support you every step of the way. For more in-depth guides, explore our Online Security & Privacy categories.